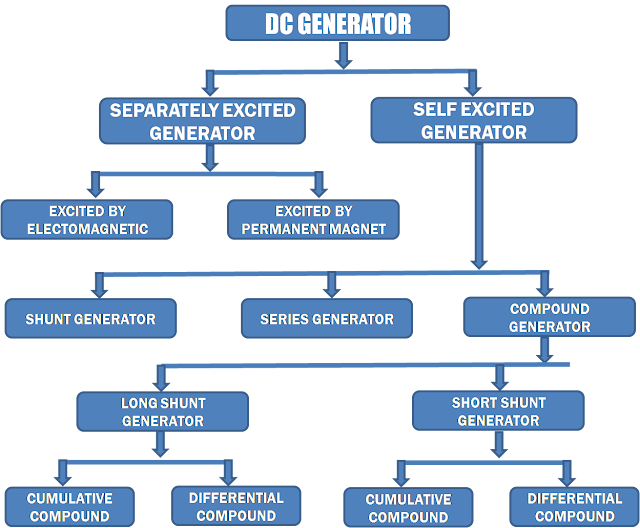
Classification of Generators is based on the method of field excitation. DC generators are classified as below :
(1)Separately Excited
Generator
Which DC generators field poles are excited by an external DC
source is known as separately excited Generator. External DC source May be independent
source such as a battery.
(2)Self Excited
Generator
Which DC generators field poles are excited by itself due to
residual magnetism is known as self excited Generator
According to construction and connection of field winding
with armature, there are 3 main types Generator:
- Series Generator
- Shunt Generator
- Compound Generator
Series Generator:
Which generator field winding connected in series with
armature winding is known as series generator.
Its field winding is made of thick wire and less number of
turns, with result that the resistance within the generator is small.
In this generator field winding, armature and load are all
connected in series, therefore same amount of current flow them.
 |
| Current Equation in Series Generator |
Series generator always started after installing the constant load on it. Because without load it will act as open circuit. Thus there is no current flow through the generator as the field winding is in series with armature.
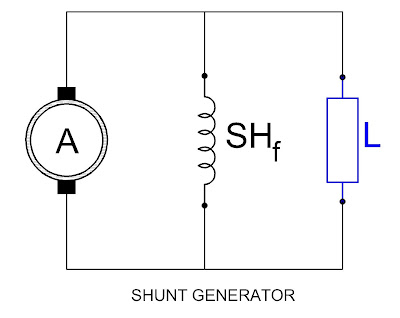
Shunt Generator:
In which generator field winding connected parallel with
armature winding known as shunt generator.
Its field winding is made of thin wire and more number of
turns, with result that the resistance of field winding is more.
Shunt generator always started without load because the emf
induced at that time is very small, if at that time load is connected the
current induced due to residual magnetism start to flow in to load not in the
shunt field winding. This is because the resistance of load is lower than field
winding and current always flow through the easiest path. Thus there will not
be sufficient current in the shunt field winding and the generator not build up
its total voltage.
In shunt generator the armature current has two parallel
paths, one through the load and other through the shunt field winding. Thus
armature current is equal to the sum of the load current and field current.
 |
| Current Equation in Shunt Generator |
Compound Generator
Combination of shunt field and series field within one generator
provides two sources of excitation, and such a generator is called compound
generator.
Compound generator is two types:
A. Long shunt compound generator
B. Short shunt compound generator
B. Short shunt compound generator
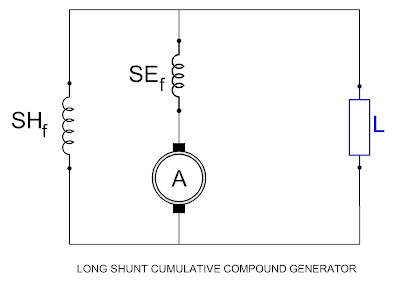
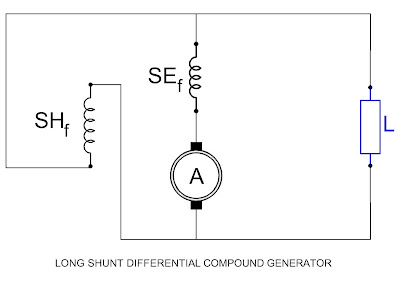
A. Long Shunt:
When the shunt field is connected in parallel with the series
combination of the armature and the series field the generator is said to be
connected as a long shunt compound generator.
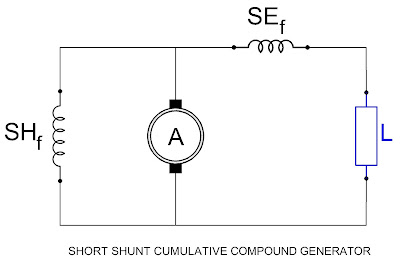
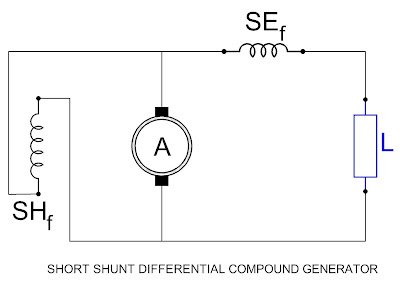
B. Short Shunt:
When the shunt field is connected in parallel with only the
armature, the generator is said to be connected as a short shunt compound
generator.
Long shunt compound generator and short shunt compound
generator further classify in two types:
(i). Cumulative compound generator
(ii) Differential compound generator
(i) Cumulative Compound Generator:
The series field coils may be connected to assist or aid the
shunt field. Then the machine is said to be a cumulative compound generator. In
a compound machine, the series field is wound directly over the shunt field
with proper separation by insulation.
(ii) Differential Compound Generator:
If the flux produced by the series field opposes
the shunt field flux then the action is called backing and the machine is said
to be a deferential compound generator.
Abbreviation used for this Article
SEf = Series Field
SHf = Shunt Field
A = Armature
L = Load
Ia = Armature Current
If = Field Current
IL = Load Current


No comments:
Post a Comment