We know Energy neither can be created nor it can be
destroyed, it can only be transferred from one form to another. A DC
generator converts mechanical energy to Electrical energy and a DC Motor
convert electrical energy mechanical energy. In DC generator input energy is in
the form of mechanical energy and the output energy in the form of Electrical
energy. On the other hand in DC Motor input energy is in the form of Electrical
energy and the output energy in the form of Mechanical energy.
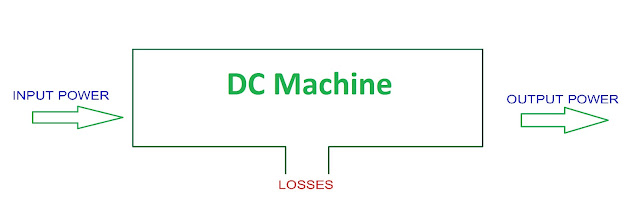
But in practical we not receive whole input energy in the
form of output energy, because some energy lost in the conversion process. The
difference between input power and output power are the losses.
(1) Copper Losses
- Armature Copper Loss
- Field Copper Loss
- Brush Contact Loss
(2) Iron losses:
- Hysteresis loss
- Eddy Current loss
(3) Mechanical Losses
- Winding loss
- Friction loss
(1)Copper Losses:
These are the losses that occur in the winding of the machine
due to flow of electric current. These losses are called copper losses because armature
and field windings are made of copper.
(i) Armature Copper Loss = Ia2Ra
Where, Ia = Armature Current
Ra = Armature Resistance
(ii) Field Copper Loss =
In Series field winding = Ise2Rse
Where, Ise = Series Field Current
Rse = Series field Resistance
In Shunt field winding = Ish2Rse
Where, Ish = Shunt field Current
Rsh = Shunt field Resistance
(iii)Brush Contact Loss : This loss occurs due to brush contact
resistance (between the surface of brush of brush and surface of the
commutator). loss is included in the armature copper loss.
(2)Iron losses:
These take place in the armature due to rotation of its iron
core in the magnetic field. These are also called magnetic or core losses and
consist of Hysteresis loss and Eddy current loss which are elaborated below.
(i) Hysteresis loss: This loss occurs in the core due to
magnetization, demagnetization and again magnetization of the core in the
reverse direction. Hysteresis loss depends upon the frequency, flux density, volume
and type of the core.
Wh = η Bmax1.6fV
Where,
η = Hysteresis
coefficient depending upon the material (constant)
Bmax = Maximum value of flux density in
webers/metre2
f = Number of magnetic reversals per second (i.e. frequency)
V = Volume of the magnetic core
Wh = Power loss in watt/ metre2 due to hysteresis
Note: 4% silicon steel is used to reduce the hysteresis loss.
(ii) Eddy Current loss
: This loss take
place in the armature core when it is rotated in the magnetic field Therefore,
heavy currents flow through them which is due to the induced emf. To decrease
the eddy current loss, the cores are made from thin sheets pressed together.
Eddy currents loss is given as :
We = η B2maxf2t2
Where,
Bmax = Maximum value of flux density in
webers/metre2
f = Number of magnetic reversals per second (i.e. frequency)
t = Thickness of lamination
We
= Eddy current loss in watts
(3) Mechanical Losses:
Mechanical losses are consist of air friction of
rotating armature, bearing friction, brush friction.

No comments:
Post a Comment